For the high-temperature preparation of oxidation-sensitive materials like titanium alloys and high-purity alumina ceramics, a clean-type vacuum box furnace is an indispensable tool. By providing a controlled vacuum environment, uniform heating, and clean protective atmospheres, it ensures material purity, reproducibility, and superior performance.
Author Archives: ZYLAB Solution
Forming is a critical stage in powder metallurgy (PM) that determines the geometry, density, and strength of the final sintered product. During this step, loose metal powders are compacted or shaped into a defined geometry known as the green compact, which is later densified through sintering.
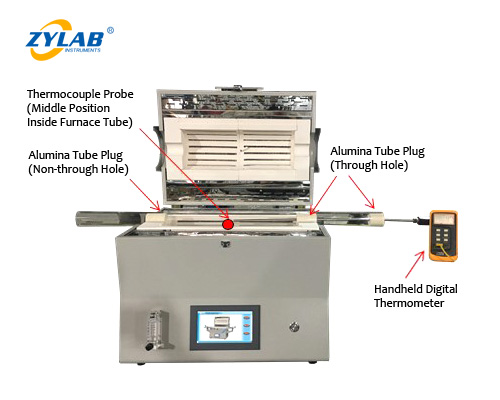
To ensure measurement accuracy, researchers often use a handheld K-type armored thermocouple and digital thermometer. This tool allows users to:
Verify the actual temperature inside the furnace tube.
Measure the surface temperature of the sample during heat treatment.
Calibrate the tube furnace temperature system for improved precision.
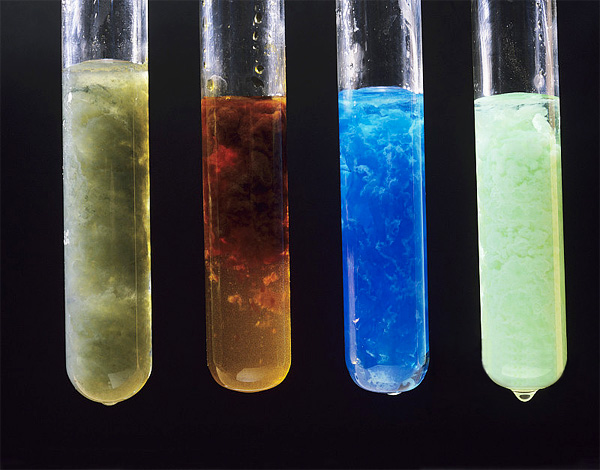
Following Part 1: Mechanical Milling Method, this second installment of the Powder Preparation Series focuses on chemical methods for producing powders. Unlike mechanical milling, which relies on physical forces, chemical methods leverage chemical reactions to synthesize powders with precise composition, controlled particle size, and uniform morphology.
Powder preparation is a fundamental step in materials science, metallurgy, ceramics, and additive manufacturing. The properties of the final product—whether it is a sintered ceramic, a metallic component, or a composite material—largely depend on the characteristics of the powders used. In this first part of our Powder Preparation Series, we will focus on one of the most widely applied approaches: the mechanical milling (mechanical pulverization) method.
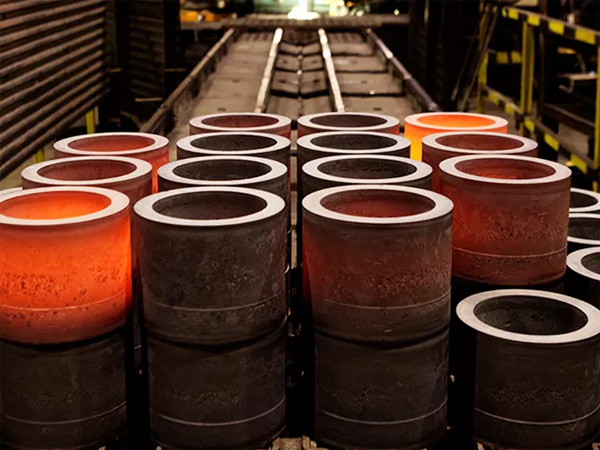
Quenching and tempering, commonly known as “tempering after quenching” or “quench-temper treatment”, is a fundamental heat treatment process used to optimize the mechanical properties of steel. This article explores what quenching and tempering is, its purpose, how it differs from simple quenching, and essential technical considerations for researchers and engineers.
While conventional heat treatment is widely applied in industries, vacuum heat treatment has become essential for high-precision and high-performance applications. This article explores the differences between conventional and vacuum heat treatment, including furnace types, process methods, and practical considerations.
While conventional heat treatment methods like annealing, normalizing, and quenching alter the bulk properties of a material, carburizing and nitriding focus on the surface layer, creating a hard, wear-resistant shell while maintaining a tough and ductile core.
At ZYLAB, we take pride in providing high-quality laboratory equipment that meets the rigorous demands of research institutions and universities worldwide. Recently, we had the opportunity to supply a Square Dry Pellet Pressing Mold to the University of Technical Malaysia Malacca (UTeM), a leading institution in materials science and engineering research.
Tempering is the essential follow-up step after quenching, ensuring metals are not only strong but also reliable in daily use. By carefully selecting the tempering temperature and furnace type, engineers can fine-tune hardness, toughness, and ductility to match specific applications.