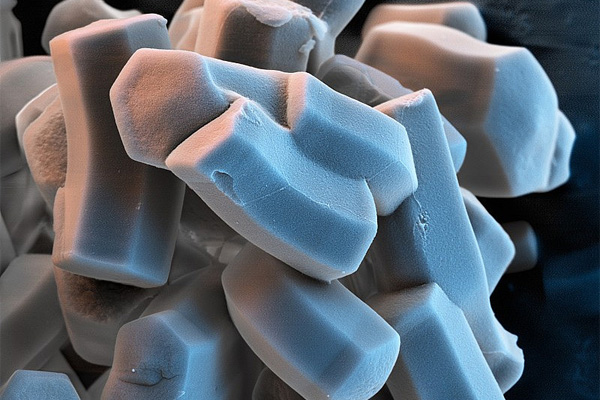
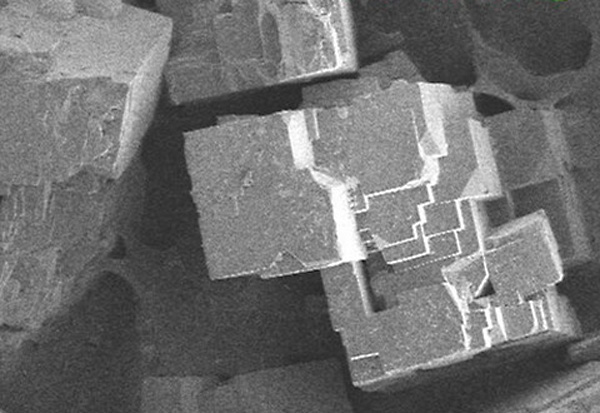
While traditional synthesis methods such as solvothermal and hydrothermal techniques dominate MOF fabrication, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) has emerged as an innovative alternative. CVD enables precise control over MOF structure and composition, enhancing scalability and functional properties.
Author Archives: ZYLAB Solution
Among the various synthesis methods, solvothermal synthesis is one of the most effective techniques for obtaining high-purity MOF powders with controlled morphology and crystallinity. This article provides a detailed guide on the solvothermal synthesis process, the required reaction equipment, and key parameters such as temperature and reaction time.
Compared to conventional methods, MSE furnaces offer higher efficiency, lower environmental impact, and improved metal purity, making them ideal for research laboratories and pilot-scale metal production.
From laboratory-scale research to large-scale industrial production, selecting the right sintering method is essential for optimizing material performance.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) has emerged as a key technology in the synthesis of advanced porous materials, including Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) and nanoscale coatings. With its ability to deposit thin films with precise control over composition and morphology, CVD plays a vital role in various industries such as energy storage, catalysis, gas separation, and biomedical applications.
The synthesis and high-temperature treatment of MOFs require precise thermal control to ensure optimal crystal formation, stability, and performance. Selecting the right laboratory furnace is essential for researchers working on MOF development.
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) furnaces are essential for thin-film deposition in industries such as semiconductors, optics, photovoltaics, and MEMS. Choosing the right PECVD furnace is crucial to achieving high-quality film coatings with precise control over deposition parameters.
Porous materials are widely used in catalysis, gas storage, separation technologies, and energy storage due to their high surface area, tunable pore structures, and excellent chemical stability. Among them, Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) and silica (SiO₂) are two of the most prominent representatives. Thermal treatment plays a crucial role in optimizing their structural and functional properties.
Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a widely used thin-film deposition technique in semiconductor manufacturing, optics, photovoltaics, and other advanced material applications. Compared to traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), PECVD offers significant advantages, particularly in achieving high-quality films at lower temperatures.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) technology is widely used in semiconductor manufacturing, optics, thin-film coatings, and material science. Within this technology, different types of CVD furnaces exist, including CVD, PECVD (Plasma-Enhanced CVD), and FBCVD (Fluidized Bed CVD).