Table of Contents
In materials science and chemical research, the ability to achieve ultra-fine, consistent particle sizes is often critical. Whether you’re developing battery materials, advanced ceramics, or pharmaceutical powders, contamination-free and efficient grinding is essential. Laboratory jet mills offer a powerful and compact solution for researchers seeking high-performance results on a small scale.
What Is a Laboratory Jet Mill?
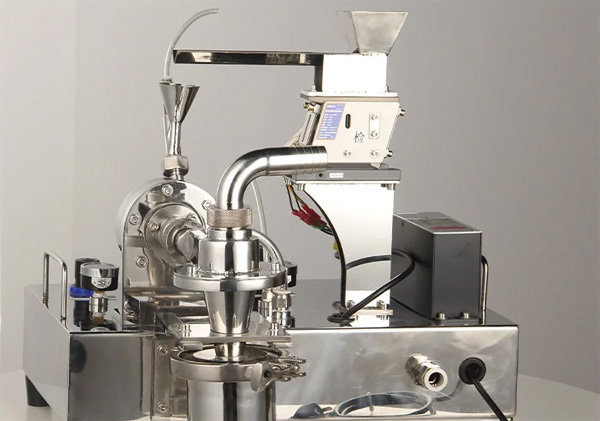
A laboratory jet mill is a small-scale powder grinding system that uses high-pressure gas—typically compressed air or nitrogen—to pulverize materials through particle-to-particle collisions. Unlike mechanical mills, jet mills do not involve moving parts for grinding, making them ideal for low-contamination, high-precision milling.
How Does It Work? Understanding the Principle
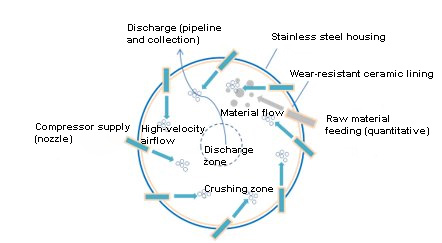
At its core, a ZYLAB Jet Mill operates on a simple yet powerful concept:
-
Gas Acceleration: Compressed air or inert gas (e.g., nitrogen) enters through the mill at high speeds (0.4–6 m³/min; 0.6–1.0 MPa).
-
Particle Collision: When particles meet in the air stream, they collide at high velocity, breaking apart via impact and viscous shear forces.
-
Cyclone Separation: Pulverized particles exit into a cyclone separator where centrifugal force sorts out fines, depositing them into collection bags or vessels .
-
Exhaust Flow: Air or inert gas exits, often through a filter or dust collector, maintaining a clean environment.
Why gas‑based milling?
-
No heat or mechanical contamination, ideal for thermosensitive and ultra-pure materials.
-
Narrow particle size distribution, enabling consistent quality across batches.
-
Minimal maintenance, as there are no rotating parts subject to wear.
Key Features of Laboratory Jet Mill
-
Compact, Tabletop Design – Optimized for laboratory benchtop use with minimal footprint.
-
Contamination-Free Milling – Ideal for high-purity materials due to lack of metal-on-metal contact.
-
Submicron Particle Sizes – Achieves D50 ≤ 0.5 µm depending on the material.
-
Low Sample Volume – Efficient milling for small quantities (gram to tens of grams).
-
Tool-Free Disassembly – Easy to clean and reassemble between batches.
-
Inert Atmosphere Option – Available for oxygen-sensitive or flammable materials.
Applications: Where It Excels
-
Advanced Ceramics: From alumina to zirconia, achieving consistent sub-micron powders.
-
Battery Materials: Crushing cathode/anode powders for Li-ion R&D.
-
Fine Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals: Processing thermosensitive APIs with high purity demands.
-
Pigment & Coating Industries: Creating ultra-fine pigments for vibrant, stable coatings.
-
Non‑mineral Materials: Refining food additives, bio-materials, and biochemical powders.
Jet Mill vs Ball Mill: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | Jet Mill | Ball Mill |
| Grinding Mechanism | Particle-particle collisions (gas jet) | Mechanical impact and friction (balls) |
| Contamination Risk | Very low (no grinding media) | Higher (from media and lining wear) |
| Particle Size | Submicron achievable | Limited to micron-level |
| Cleaning Difficulty | Easy (no media) | Moderate |
| Suitable for | High-purity, high-value materials | Bulk grinding |
| Atmosphere Control | Yes (inert gas options) | Limited |
If your application requires ultra-fine particle size, high purity, and precision, the jet mill is usually the superior choice—especially in research and development.
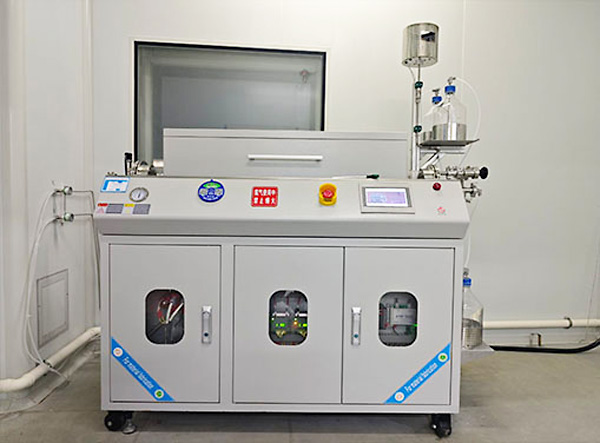
Choosing the Right Jet Mill for Your Lab
Here are some factors to consider when selecting a laboratory jet mill:
-
Target Particle Size
– Ensure the system can reach your desired fineness (e.g., D50 ≤ 1 µm). -
Sample Volume
– Select a system that supports your typical batch size, whether grams or hundreds of grams. -
Material Compatibility
– Consider the hardness, stickiness, or explosiveness of your material. ZYLAB offers PTFE- or ceramic-lined versions for reactive or corrosive materials. -
Atmosphere Requirements
– For materials sensitive to oxygen or moisture, inert gas milling is a must.
Why ZYLAB? Advantages in Every Detail
-
Clean & Contamination‑Free: Alumina-lined, stainless‑steel body, no metal wear.
-
Adjustable Feed Control: Vibrating feeder for precise dosing.
-
User‑Friendly: Compact, portable, easy setup.
-
Built for Research: Handles tiny batches of high-cost materials.
-
Support & Customization: Global supplier since 2008, serving material science, powder metallurgy, battery R&D, nanomaterials synthesis, and more.
Conclusion
For researchers and innovators working with ultra-fine powders, a laboratory jet mill offers unmatched performance in terms of cleanliness, particle control, and compact usability. ZYLAB’s solution is built to meet the challenges of modern material science—from ceramics and batteries to pharma and nanotech.
Contact us today to learn how ZYLAB’s Lab-Scale Jet Mill can accelerate your powder processing projects.
Get In Touch
Fill out the form below — free quote and professional suggestion will be sent for reference very soon!





