Table of Contents
The ZYLAB mini tube furnaces are essential equipment in modern laboratories and research facilities, widely used for high-temperature sintering, annealing, and material processing. These laboratory furnaces offer precise temperature control and a compact design, but safe and effective operation is crucial to prevent equipment damage and ensure consistent results. This article outlines key precautions and best practices for using a mini tube furnace.
Correct Placement of Samples and Insulation Plugs
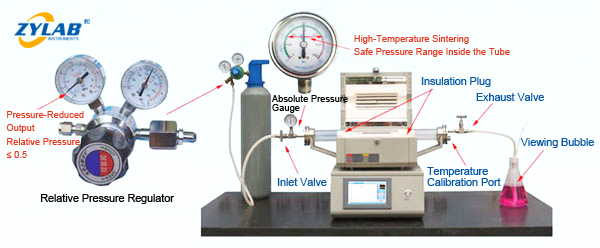
Before starting the furnace, ensure that the samples are properly placed inside the tube. Both insulation plugs must be inserted in the correct positions to maintain thermal efficiency and prevent heat loss. Use a low-pressure regulator as shown in the diagram (refer to your manual for proper connection).
Gas Flow and Pressure Settings
-
Adjust the pressure regulator to a relative pressure ≤ 0.05 MPa.
-
Open the inlet valve and monitor the absolute pressure gauge at the gas inlet.
-
When the tube’s absolute pressure reaches ≥ 0.1 MPa, fully open the exhaust valve.
-
Adjust the gas flow and observe the bubbles. Under normal protective atmosphere, a bubble rate of 5–60 bubbles per minute is recommended.
Monitoring During the Sintering Process
During sintering, continuously observe the exhaust side for bubbles:
-
If no bubbles appear, it may indicate a blockage at the exhaust due to contamination – stop the furnace and clean immediately.
-
Or insufficient gas supply – replace the gas cylinder as needed.
Important: Never continue operation if the exhaust is blocked, as this can damage the quartz or alumina tube.
Maintaining Safe Pressure in High-Temperature Tubes
When using high-purity quartz tubes or alumina tubes at high temperatures, keep the absolute pressure inside the tube between 0.05 MPa and 0.15 MPa. Exceeding this range increases the risk of tube breakage and furnace damage.
Accurate Temperature Measurement
The displayed temperature on the mini tube furnace may differ from the actual temperature at the sample point. Use the temperature calibration port with a handheld thermometer to verify the real-time temperature at various sintering stages, ensuring precise control for high-temperature sintering experiments.
Avoid Contamination from Alkali Metal Ions
Alkali metal ions such as K, Na, Li, Ca, and Mg can crystallize at high temperatures, causing serious damage to quartz tubes. Always ensure your samples are free from these contaminants before sintering.
Programming the Sintering Curve
Set the sintering program in minutes using the format:
“Start Temperature – Sintering Time – Target Temperature”
After completing the curve setup, enter “END” for the designated time period to finalize the program. Proper programming ensures consistent sintering results and extends the life of your laboratory furnace.
Conclusion
Using a mini tube furnace safely requires careful attention to pressure control, gas flow, temperature calibration, and material purity. Following these precautions will help you achieve reliable high-temperature sintering results, protect the furnace from damage, and maintain a safe laboratory environment. Regular inspection and proper operation are key to maximizing the lifespan and performance of your laboratory tube furnace.
Get In Touch
Fill out the form below — free quote and professional suggestion will be sent for reference very soon!